 Course Transcript
Course Transcript Image Processing
 Course Transcript
Course Transcript  Course Transcript
Course Transcript Beyond the Visible – EnMAP data access and image preprocessing techniques
 Course Transcript
Course Transcript Beyond the Visible – Introduction to Hyperspectral Remote Sensing
 Course Transcript
Course Transcript Beyond the Visible – Imaging Spectroscopy for Agricultural Applications
 Tutorial
Tutorial Large-scale EO data handling
 Tutorial
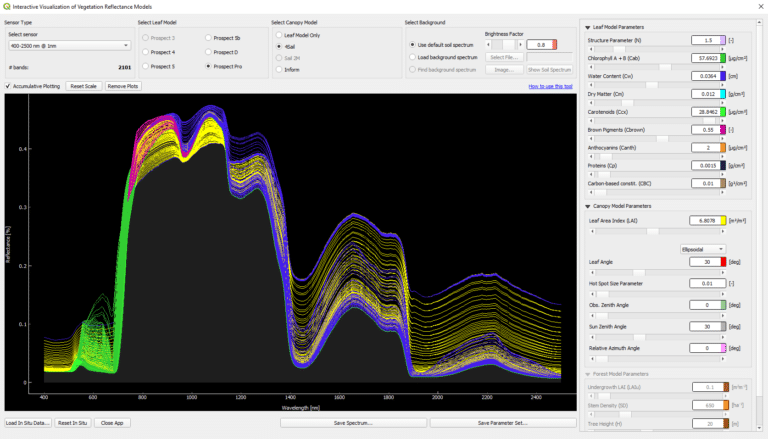
Tutorial Interactive Visualization of Vegetation Reflectance Models (IVVRM)
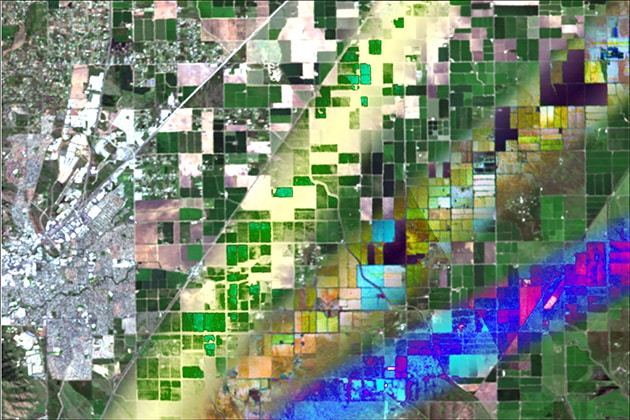 Unit
Unit Retrieval approaches of vegetation traits from imaging spectroscopy data
 Unit
Unit Dimensionality reduction of imaging spectroscopy data
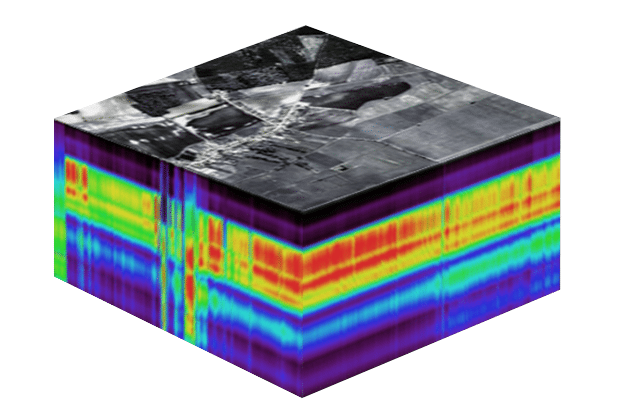 Unit
Unit Principles of imaging spectroscopy
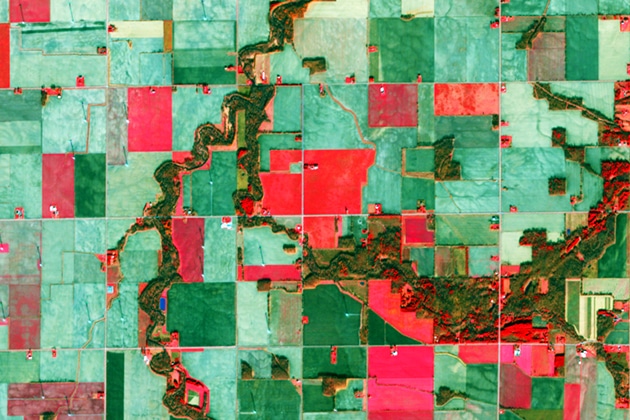 Unit
Unit Land Cover Classification
 TalkTutorial
TalkTutorial SAR Processing and Data Analysis
 Talk
Talk Procesamiento y análisis de datos de SAR
 Tutorial
Tutorial SNAP – First Steps
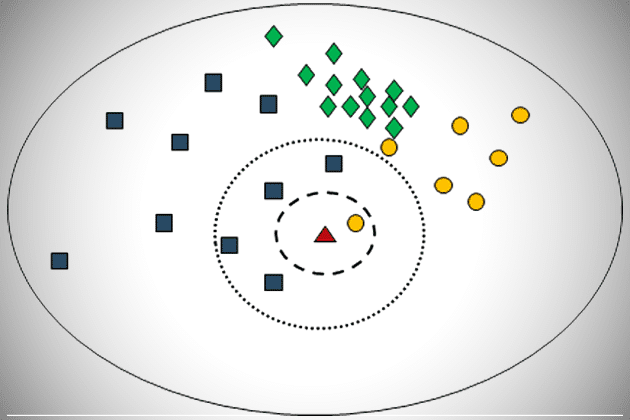 Unit
Unit Classification
 Unit
Unit Change Detection
 Unit
Unit Data fusion
 Unit
Unit Object based image analysis
 Unit
Unit Speckle filtering
 Unit
Unit Texture
 Unit
Unit 
