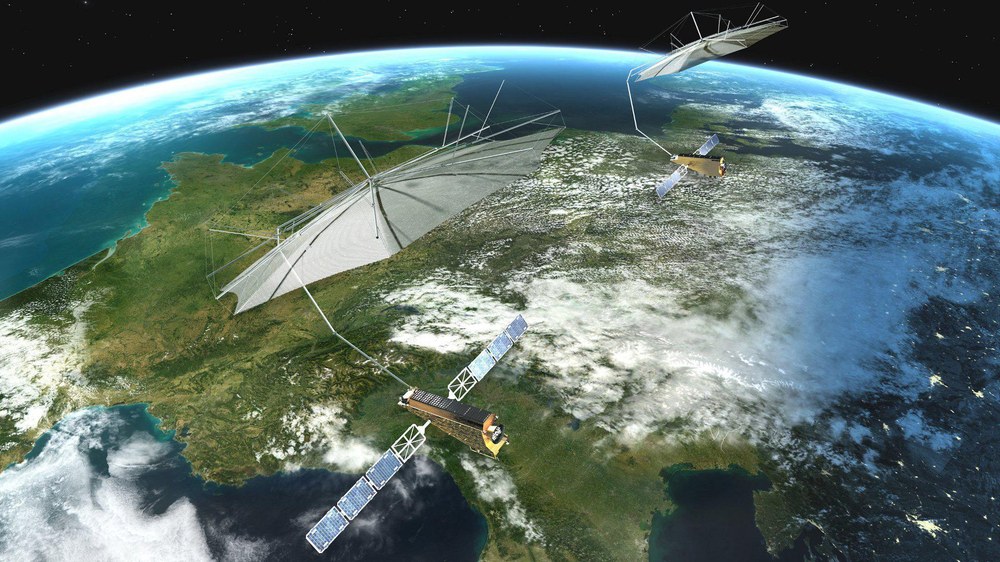
Introduction
The Tandem-L mission is an ambitious Earth observation project led by the German Aerospace Center (DLR). It aims to revolutionize our ability to observe and understand dynamic processes on Earth by leveraging advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) technology operating in the L-band frequency range. Tandem-L addresses critical scientific and societal challenges, including the monitoring of climate change, ecosystem dynamics, geophysical hazards, and the sustainable management of natural resources.
Building on Germany’s long-standing expertise in radar remote sensing—demonstrated through missions such as TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X—Tandem-L represents a significant leap forward. With its dual-satellite configuration, the mission will deliver unprecedented temporal and spatial resolution, enabling the continuous observation of Earth system processes at scales previously unattainable.
Mission Objectives
The core scientific objectives of Tandem-L focus on advancing our understanding of the dynamic Earth system. These include:
- Global Biomass Monitoring: Quantifying global forest biomass and detecting changes over time to enhance our understanding of the carbon cycle. These measurements will support efforts to mitigate climate change by providing critical data for carbon accounting and assessing forest degradation.
- Surface Deformation Mapping: Monitoring ground deformations caused by earthquakes, landslides, subsidence, volcanic activity, and other geophysical processes with sub-centimeter accuracy. Tandem-L’s high-resolution deformation data will improve early warning systems and risk assessments.
- Dynamic Surface Process Observation: Capturing rapid changes in glaciers, ice sheets, and permafrost, as well as soil moisture dynamics and vegetation structure. This will inform climate models and support hydrological studies.
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Generation: Producing high-accuracy, up-to-date DEMs at regional and global scales. These models are essential for applications ranging from flood modeling to urban planning and disaster management.
In addition to these primary objectives, Tandem-L will serve as a valuable platform for testing new radar techniques and advancing SAR science.
Mission Concept and Technical Approach
Tandem-L will consist of two identical satellites operating in close formation, separated by a few hundred meters to a few kilometers. This formation flying approach enables advanced SAR imaging techniques that dramatically enhance data quality and scientific value:
- Single-Pass Interferometry (InSAR): The dual-satellite system allows for simultaneous observations of the same ground area, eliminating temporal decorrelation and atmospheric noise. This results in highly accurate 3D surface maps and deformation measurements.
- High Temporal Sampling: Tandem-L is designed to revisit and image any point on Earth every 8 days or less. The mission’s flexible orbit design and formation flying capabilities allow for more frequent acquisitions in targeted regions.
- Polarimetric SAR (PolSAR) and Tomographic SAR (TomoSAR): Tandem-L incorporates full polarimetric capabilities and advanced tomographic processing to resolve vertical structures in forests and urban areas, as well as providing detailed vegetation and soil moisture characterization.
Key Technologies
- L-Band Radar: Operating in the 1.2 GHz frequency range, the L-band radar system offers deep penetration into vegetation canopies, soil layers, and snow. This makes Tandem-L particularly well-suited for monitoring biomass, subsurface movements, and ice masses.
- Digital Beamforming (DBF) and SAR Tomography: Advanced digital signal processing enables high-resolution imaging and 3D reconstruction of volumetric targets such as forest canopies and urban infrastructure.
- Precision Formation Flying: Autonomous formation control and relative positioning of the two satellites are essential for achieving the necessary baseline stability and imaging geometry. Tandem-L will leverage heritage technology from the TanDEM-X mission while incorporating further advancements in propulsion and navigation.
Applications and Use Cases
The wide range of applications supported by Tandem-L data underscores its importance as a multipurpose Earth observation mission:
- Climate Change and Carbon Cycle Research: Tandem-L’s global biomass datasets will enhance carbon flux models and support international agreements such as the Paris Agreement and REDD+ initiatives aimed at reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation.
- Geohazard Monitoring and Disaster Risk Reduction: By detecting ground deformation at high spatial and temporal resolution, Tandem-L will provide actionable intelligence for disaster preparedness and emergency response related to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, landslides, and subsidence events.
- Forestry and Land Use Management: Detailed biomass and forest structure measurements will inform forest management practices, support biodiversity conservation, and aid in sustainable land use planning.
- Agricultural Monitoring and Water Resource Management: Tandem-L’s ability to measure soil moisture and crop conditions at large scales will facilitate precision agriculture and efficient irrigation planning, contributing to food security and water conservation.
- Cryosphere Research: Regular monitoring of glaciers and ice sheets will improve understanding of ice mass balance and its contribution to sea-level rise. Tandem-L’s observations of permafrost dynamics will inform models of greenhouse gas emissions from thawing soils.
Strategic Importance
Tandem-L solidifies Germany’s leadership in radar remote sensing and complements existing and planned international missions, including ESA’s Biomass and NASA’s NISAR. While other missions focus on specific aspects of Earth observation, Tandem-L’s unique combination of high temporal resolution, large-scale coverage, and advanced imaging modes positions it as a cornerstone of the global Earth observation infrastructure.
By adopting an open data policy for scientific users and fostering international collaboration, Tandem-L will significantly contribute to global initiatives aimed at environmental monitoring, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development.
Current Status and Outlook
Tandem-L has successfully completed its Phase A study, including comprehensive feasibility analyses, system design definitions, and user requirements reviews. The mission awaits final approval and funding to proceed to the implementation phase.
Pending approval, the development and launch of Tandem-L could occur within the next decade. Once operational, the mission will offer transformative capabilities in radar remote sensing, advancing our ability to understand and manage Earth’s dynamic processes.
Conclusion
Tandem-L represents a bold step forward in the evolution of spaceborne radar remote sensing. By combining cutting-edge L-band SAR technology with dual-satellite formation flying, Tandem-L will provide unparalleled insights into the Earth’s surface and its dynamic changes.
From climate change research and disaster risk reduction to resource management and urban planning, Tandem-L’s data products and services will support a wide array of scientific, societal, and policy-oriented applications. As a flagship mission in Germany’s Earth observation program, Tandem-L has the potential to make lasting contributions to global sustainability and environmental stewardship.
Expand Your Knowledge – Dive Deeper
- Echoes in Space We particularly recommend topics Introduction to Interferometry and Introduction to Polarimetry