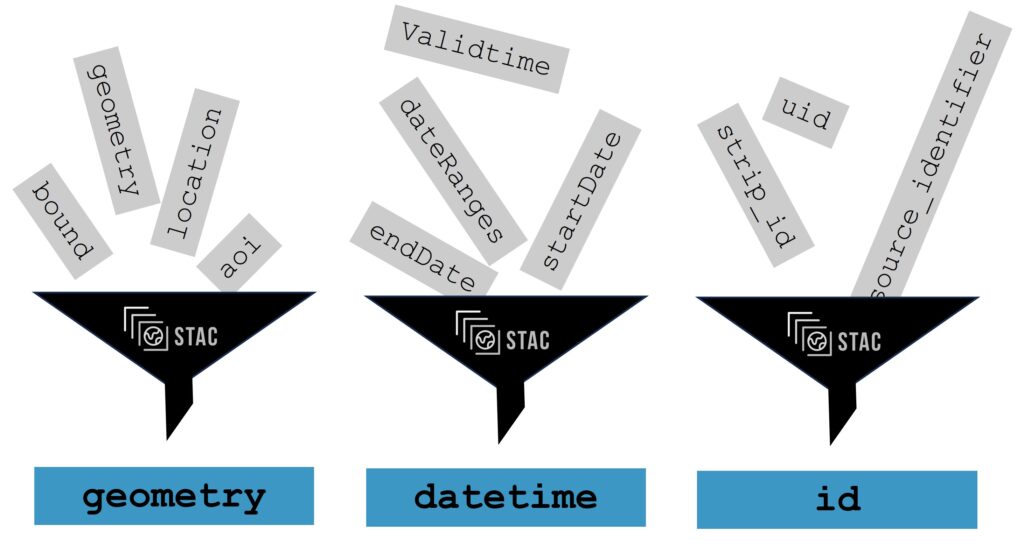
What are data properties and metadata? Copy
Data properties and metadata are sets of characteristics of geospatial data that serve different purposes. Commonly data properties are seen as attributes describing the image itself whereas, on the other hand, metadata describes the properties of a product.
Data Properties: Data properties refer to the characteristics and attributes of the geospatial data itself. These properties describe the actual content, structure, and values within the dataset. For raster data, properties can include information such as pixel values, cell size, spatial resolution, number of bands, and data format. For vector data, properties may include attributes associated with points, lines, or polygons, such as feature identifiers, names, classifications, or numerical values. Data properties are essential for understanding the data at a fundamental level and are used in the analysis, visualization, and processing tasks.
Metadata: Metadata, on the other hand, provides descriptive information about the data product. It serves as documentation that complements the data properties and offers additional context and details about the data. Metadata describes the origin, and characteristics, and helps with usage of the data, allowing users to discover, evaluate, and effectively utilize the data. It typically includes information such as the data source, acquisition parameters, coordinate reference system, temporal coverage, quality measures, and data access policies. Metadata plays a crucial role in data management, data sharing, and data interoperability by providing the necessary documentation and context for understanding and utilizing the data.
Both together provide a complete description of the data of our interest and how to work with them. Standardized ways how to describe metadata and data properties allow geospatial systems to work with data easily.