Resample Copy
In a resampling processes (e.g. resample_cube_spatial, resample_cube_temporal), the layout of a certain dimension is changed into another layout, most likely also changing the resolution of that dimension. This is done by mapping values of the source (old) datacube to the new layout of the target (new) datacube. During that process, resolutions can be upscaled or downscaled (also called upsampling and downsampling), depending on whether they have a finer or a coarser spacing afterwards. A function is then needed to translate the existing data into the new resolution. A prominent example is to reproject a datacube into the coordinate reference system of another datacube, for example in order to merge the two cubes.
Simplified: resample(🖼️, downscale) => 🟦
resample(🌍, reproject) => 🗺️
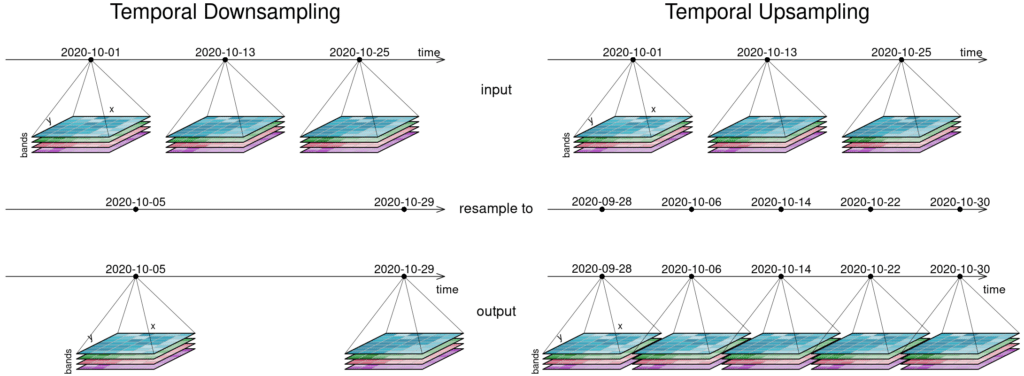
The first figure gives an overview of temporal resampling. How exactly the input timesteps are rescaled to the output timesteps depends on the resampling function.
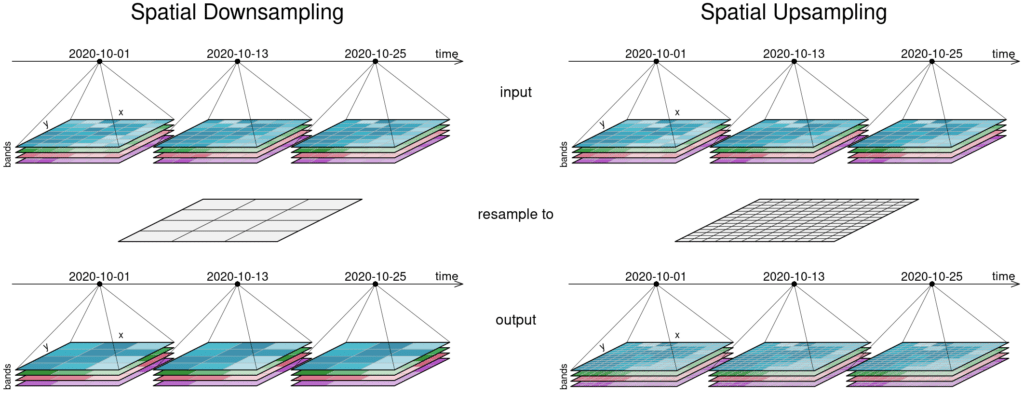
The second figure displays spatial resampling. Observe how in the upsampling process, the output datacube has not gained in information value. The resulting grid still carries the same pixel information but in a higher spatial resolution. Other upsampling methods may yield smoother results, e.g. by using interpolation.
Learn how to use Resample operators with this interactive exercise:

